“The most significant threat to global child health from SARS-CoV-2 is unlikely to be related to COVID 19 in children, but rather the socio-economic consequences of a prolonged pandemic.”1
The Child Health Task Force is a global network of implementing organizations; NGOs; academic institutions; UN, multilateral, and bilateral agencies; in-country partners; and individuals working together to support the delivery of high quality child health services.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we will continue to convene and coordinate stakeholders to share knowledge and innovative solutions to programmatic issues to stem the direct and indirect impact of the pandemic on children. We will collaborate with our partners to develop new tools and improve existing ones, and work with country partners to translate evidence about the pandemic into stronger child health programs, enabling children to survive and thrive during and after the pandemic.
Check out our webinar series:
Hosted by the Child Health Task Force, each webinar is led by a subgroup and focuses on how they are responding to the pandemic in their thematic area at the global and country level.
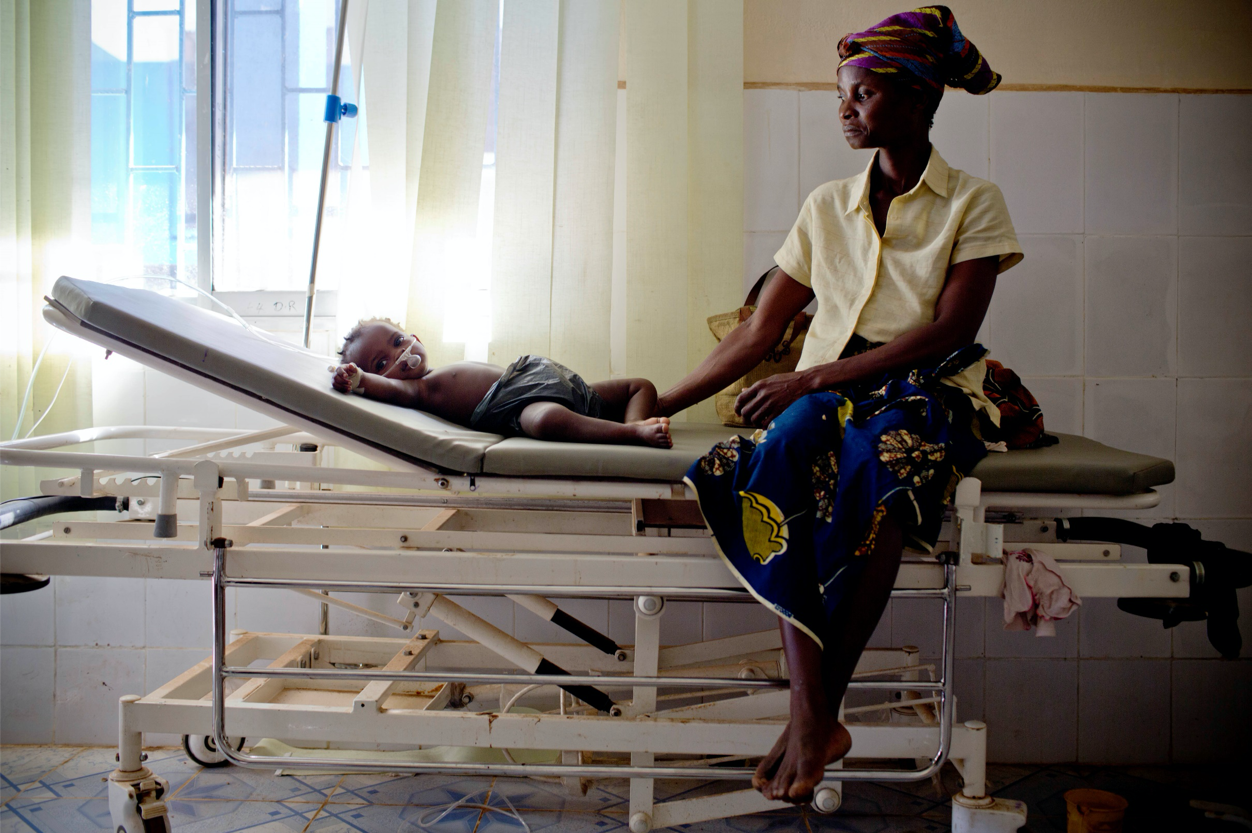
What We Know
![]()
Much of the published data and focus of the COVID-19 pandemic has been on adult patients, leaving behind a large knowledge gap for child health service providers and global partners assisting in the pandemic response. The body of information regarding clinical features of the coronavirus in children and adolescents is growing, but questions remain.
- Children of all ages are susceptible to COVID-19 and like adults, can transmit the virus to others. Children are increasingly recognized as playing a role in the community spread of COVID-19 and social distancing measures continue to be recommended for all ages.1,9,10
- Pediatric cases account for 2.1-7.8% of confirmed COVID-19 cases according to national statistics from countries in Asia, Europe and North America. However, the prevalence of COVID-19 in children globally is still not well understood. This may be due to the fact that children are more likely to present milder symptoms or asymptomatic which leads to underdiagnosis and undertesting.4
- While COVID-19 is often milder in children than adults, in some cases it can progress to severe disease. For example, newborns with certain underlying medical conditions are at greater risk for developing severe illness from COVID-19.2,3
- Adolescents and children above 10 years old transmit the SARS-CoV-2 virus as often as adults and more often than children under 10. After the reopening of schools in France, England, Israel, and Chile, a rapid spread of the virus was observed in secondary and high schools, while limited spread was observed in primary schools.11
- Reported cases of children with COVID-19 associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) have increased in Europe, North America, Asia, and Latin America. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children is a condition associated with COVID-19 where organs of the body become inflamed. MIS-C can lead to multiple organ failure and long term health effects, most of which are unknown.4
- Children are disproportionately affected by many of the unanticipated impacts of the pandemic. The climate of fear and economic uncertainty impacts children’s health, as parents or family members delay care-seeking for other childhood illnesses and routine vaccinations.9,14 Nationwide lockdowns and school closures have had a negative impact on child and adolescent mental health globally.5
- The pandemic poses additional challenges for children in low and middle income countries (LMICs), including diversion of resources away from child health, lack of access to PPE, and a high prevalence of risk factors for severe respiratory infection such as HIV and malnutrition.6 LMICs also experience greater disruptions of essential services than high-income countries do, directly impacting care for children and adolescents.12 The pandemic amplifies existing health inequities faced every day by marginalized communities, children and their families.13
For more information, UNICEF has developed a data hub sharing up-to-date scientific information on COVID-19 and children. Save the Children also published a comprehensive report capturing children's and their caregivers' voices from 37 countries in September 2020: Protect a Generation: The impact of COVID-19 on children's lives. Access the report on our website here.
Points taken from featured journal articles here. The information was last updated February 18, 2021.
Additional Research Needs Include
![]()
- Understanding the differences in clinical features of COVID-19 by age.
- Gathering data on predictors of mortality in children and the severity of the disease in children with underlying conditions like malnutrition, rheumatic heart disease, or HIV positive children.
- Monitoring the indirect impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on child health and development.
- Understanding the impacts of school closures and quarantine on child and adolescent physical and mental health.
- Understanding the long-term health outcomes of COVID-19 infection in children, especially those suffering from MIS-C.
Featured Journal Articles
![]()
- Clinical manifestations of children with COVID‐19: A systematic review
- From SARS to COVID-19: What we have learned about children infected with COVID-19
- For Parents: Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) associated with COVID-19
- COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents
- Impact of COVID-19 and lockdown on mental health of children and adolescents: A narrative review with recommendations
- Challenges of COVID-19 in children in low- and middle-income countries
- The Direct and Indirect Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infections on Neonates: A Series of 26 Cases in Bangladesh
- Impact of Covid-19 on Children’s Education in Africa
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Children - What We Know So Far and What We Do Not?
- SARS-CoV-2 infections in children and young people
- On the effect of age on the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in households, schools and the community
- Pulse survey on continuity of essential health services during the COVID-19 pandemic
- COVID-19 pandemic: health inequities in children and youth
- Childhood vaccinations: Hidden impact of COVID-19 on children in Singapore.
Please click here for more articles related to child health and COVID-19.
COVID-19 Resources for Child Health Stakeholders
![]()
We have identified key resources that child health stakeholders should be aware of in order to best support countries to continue providing life-saving child health services during the COVID-19 pandemic. Please email childhealthtaskforce@jsi.com with any additional resources to feature on this page.
Please note that the Child Health Task Force has not created these materials and all rights belong to the authoring organizations.
- Operational Guidance
- Operational Planning Guidelines to Support Country Preparedness and Response: WHO's overarching practical guide for UN Country Teams and partners to develop a COVID-19 strategic Preparedness and Response Plan to provide immediate support to national governments to prepare for and respond to COVID-19.
- Maintaining Essential Health Service - Operational Guidance for the COVID-19 Context: This document recommends practical actions that countries can take at national, subregional and local levels to reorganize and safely maintain access to high-quality, essential health services in the pandemic context. This document supersedes the earlier Operational guidance for maintaining essential health services during an outbreak and complements the recently-released Community-based health care, including outreach and campaigns, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Continuing essential sexual reproductive, maternal, neonatal, child and adolescent health services during COVID-19 pandemic - practical considerations: This document builds upon the previous Regional Guidance published, which provided high-level guidance to countries for continuing good quality and equitable sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn, child, and adolescent health (SRMNCAH) services during the COVID19 pandemic. It provides principles, strategic actions and a few examples of operational actions that countries have found useful for preparing plans to continue prioritized SRMNCAH services during the pandemic. The present document includes practical operational actions for possible redesigning and modifications of essential services for different areas of SRMNCAH life-course continuum, within the continuity plans prepared by the countries.
- Interim Guidance for COVID-19 Prevention and Control in Schools: WHO, UNICEF and IFRC recommend clear and actionable guidance for school administrators, teachers and staff; caregivers and parents; as well as students and children. The recommendations focus on safe operations through the prevention, early detection and control of COVID-19 in schools and other educational facilities. UNICEF also offers supplemental guidance materials in English, Spanish, French and Portuguese on a range of topics from cleaning and supply to mental health and psychosocial support to the protection of children in and out of school in the context of COVID-19.
- Clinical Guidance
- Clinical Management of COVID-19 - Interim Guidance: This WHO guidance document is intended for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients during all phases of their disease (i.e. screening to discharge). This update has been expanded (Previous version: Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when COVID-19 is suspected) to meet the needs of front-line clinicians and promotes a multi-disciplinary approach to care for patients with COVID-19, including those with mild, moderate, severe, and critical disease.
- Clinical Care of Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) Toolkit - COVID-19 Adaptation: This toolkit is intended for clinicians working in acute care hospitals in low- and middle-income countries, managing adult and paediatric patients with acute respiratory infection, including severe pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis and septic shock.
- Clinical Care Guidance, Children with COVID-19: This guidance from the U.S. Center's for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides healthcare providers with up to date information available on children with COVID-19 and current treatment practices for managing pediatric patients.
- WHO Case Report Form and Scientific Brief: Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents temporally related to COVID: In response to reports from Europe and North America describing clusters of children with a multisystem inflammatory condition potentially linked to COVID-19 and the urgent need for collection of standardized data describing clinical presentations, severity, outcomes, and epidemiology, WHO has developed a preliminary case definition and case report form for multisystem inflammatory disorder in children and adolescents and encourages pediatricians across the world to use this form to report these cases if seen.
- Paediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 (PIMS) - guidance for clinicians: This document for clinicians, which has been developed after expert review of the cases, includes a case definition and approach to clinical management.
- Regional & Country Information
- WHO/AFRO COVID-19 Technical Documents: The WHO Regional Office for Africa has a comprehensive list of technical documents on important topics for countries in the region, such as case management, IPC, continuity of essential services, coordination at points of entry, holding elections, and COVID-19 Q&As.
- Compendium of Resources to Support COVID-19 Response in LMICs: PATH has compiled a list of resources geared towards LMICs that includes key technical and policy guidance as well as resources to maintain essential health services, support evidence-informed policy making, data-driven decision-making, and to see what other countries are doing.
- ECOWAS COVID-19 Dashboard
- OECD Country Policy Tracker
- Ethiopia
- Kenya
- Nigeria
- Pakistan
- Zambia
- Community Care & CHWs
- Interim Guidance - Community-based health care, including outreach and campaigns, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic: This guidance, developed by the IFRC, WHO, and UNICEF, outlines the role of community-based health care and adaptations to keep people safe, maintain the continuity of essential services, and ensure an effective response to COVID-19.
- Preparedness for and response to coronavirus disease (COVID-19): This tool is designed to support risk communication, community engagement (RCCE) staff working with national health authorities, as well as other partners, to develop, implement and monitor an effective action plan for communicating effectively with the public during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak.
- Community Health Impact Coalition’s CHW COVID-19 Workflow Resources: This dynamic document compiles resources from hundreds of organizations on a wide range of technical areas relevant to CHWs and specific country contexts. Led by Community Health Impact Coalition, the group meets weekly and frequently updates these set of resources.
- Commodities & the Supply Chain
- WHO COVID-19 Essential Supplies Forecasting Tool: The WHO COVID-19 Essential Supplies Forecasting Tool (ESFT) is designed to help governments, partners, and other stakeholders to estimate potential requirements for essential supplies to respond to the current pandemic of COVID-19.
- WHO’s Emergency Global Supply Chain System (COVID-19) catalogue: This catalogue lists all medical devices, including personal protective equipment, medical equipment, medical consumables, single use devices, laboratory and test-related devices that may be requested through the COVID-19 Supply Portal.
- COVID-19’s Impact on Health Product Supply- Assessment & Recommendations: This document is regularly updated by the Global Fund to contain their most recent assessment of COVID-19's impact on core health product supplies and recommendations for implementing partners on how to manage the impact.
- Digital Health
- WHO's COVID-19 Mobile Learning App for Health Workers: This app provides health workers everywhere with an efficient way to access the WHO's COVID-19 knowledge resources all in one place, including up-to-the-minute guidance, tools, training, self-paced learning, and virtual workshops to support health workers in caring for patients infected by COVID-19 - as well on how they can protect themselves as they do their critical work. The app's content is available in six languages - Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian and Spanish and can be downloaded for free in the Apple App Store or Google Play Store.
- Emergencies & Humanitarian Settings
- Interim Guidance - Public Health and Social Measures for COVID-19 Preparedness and Response Operations in Low Capacity and Humanitarian Settings: This Interim Guidance from the IASC, outlines how key public health and social measures needed to reduce the risk of COVID-19 spread and the impact of the disease can be adapted for use in low capacity and humanitarian settings. The Guidance is intended for humanitarian and development actors of all operational levels working with communities, as well as local authorities involved in COVID-19 preparedness and response operations in these settings, in support of national and local governments and plans.
- COVID-19 & Humanitarian Crises: This open-access web-based platform promotes the exchange of field-based COVID-19 program adaptations and innovations, facilitating learning among organizations in different sectors and contexts. Run by the Johns Hopkins Center for Humanitarian Health, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, and Geneva Centre of Humanitarian Studies.
- COVID-19 and Fragile Settings: This policy brief was published December 2020 and developed by UHC2030 International Health Partnership's Fragile Settings Technical Working Group. The paper presents: 1. Global guidance on COVID-19 response strategies that should be adapted to context-specific and evolving needs in fragile settings, 2. An urgent call to protect funding for health in fragile settings, 3. Six emergent lessons to enhance COVID-19 response and recovery in fragile settings.
- Nutrition
- The Hidden Impact of COVID-19 on Children's Health and Nutrition: This report is informed by Save the Children's global research series to generate rigorous evidence on how the COVID-19 pandemic and measures implemented to mitigate it are impacting children’s health, nutrition, learning, wellbeing, protection, family finances and poverty. Data was collected from 31,683 parents and caregivers and 13,477 children ages 11 to 17 from 46 countries, resulting in the largest and most comprehensive survey of children and families during the COVID-19 crisis to date. The report focuses on the findings and recommendations on access to food and nutrition as well as infant and young child feeding.
- FAQ & Decision Tree: Breastfeeding & COVID-19 for Healthcare Workers: This FAQ complements the WHO interim guidance: Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected and provides responses to questions that have arisen about the recommendations.
- Infant and Young Child Feeding Recommendations When COVID-19 is Suspected or Confirmed: A new counselling package has been developed in collaboration between UNICEF and USAID Advancing Nutrition, with technical support from the Infant Feeding in Emergencies (IFE) Core Group, represented by Save the Children and Safely Fed Canada. The package includes 10 Counselling Cards and a Recommended Practices Booklet, reflecting global guidelines. The package provides both easy-to-understand recommended practices for counselors and user-friendly graphics that can be used with low-literacy communities in different contexts.
- Operational guidance on Nutrition Sectoral/Cluster Coordination in the context of COVID-19: The purpose of this document is to guide Nutrition Sector/Cluster coordination mechanisms at the national level on the adaptation of the core cluster coordination functions and working modalities, due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Private Sector Engagement
- External Guidance on Private Sector Engagement for COVID-19 Response: This document outlines USAID's response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the private sector role in the response, and how the private sector can engage with USAID to support the immediate health response and second-order impact engagement.
- A Case for Local Pharmaceutical Manufacturing in Africa in Light of the COVID-19 Pandemic: This paper discusses the issue of scaling up the local pharmaceutical production in Africa as an opportunity, as well as a necessity, to tackle local epidemics of malaria, tuberculosis and HIV, as well as non-communicable diseases whose control could be undermined by the scale of the COVID-19 outbreak.
- Engaging the Private Sector in the COVID-19 Response: Impact for Health has put together this resource hub for information regarding private sector engagement and COVID-19.
- Children with Disabilities
- COVID-19 Response: Considerations for Children and Adults with Disabilities: This guidance developed by UNICEF highlights the unique impact of COVID-19 on Persons with Disabilities. Actionable steps to protect them involve the deliberate inclusion of Persons with Disabilities in every stage of the COVID-19 response.
- The Hidden Impact of COVID-19 on Children and Families with Disabilities: This report is informed by Save the Children's global research series to generate rigorous evidence on how the COVID-19 pandemic and measures implemented to mitigate it are impacting children’s health, nutrition, learning, wellbeing, protection, family finances and poverty. The results and recommendations shared in this resource focus on the various impacts of COVID-19 on children and parents/caregivers with disabilities and their families.
For a comprehensive suite of COVID-19 information,
check out the Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center.


