When sharpening and revising child health plans, countries must first agree on which activities to prioritize. Prioritization exercises can help ensure funds are purposefully allocated and that resources and interventions are strategically selected, leading to more relevant action plans. Criteria for prioritization should be clear and informed by data and outcomes from previous review and analysis activities (e.g. situational analysis, bottleneck analysis, etc.), as well as consultations with multiple stakeholders.
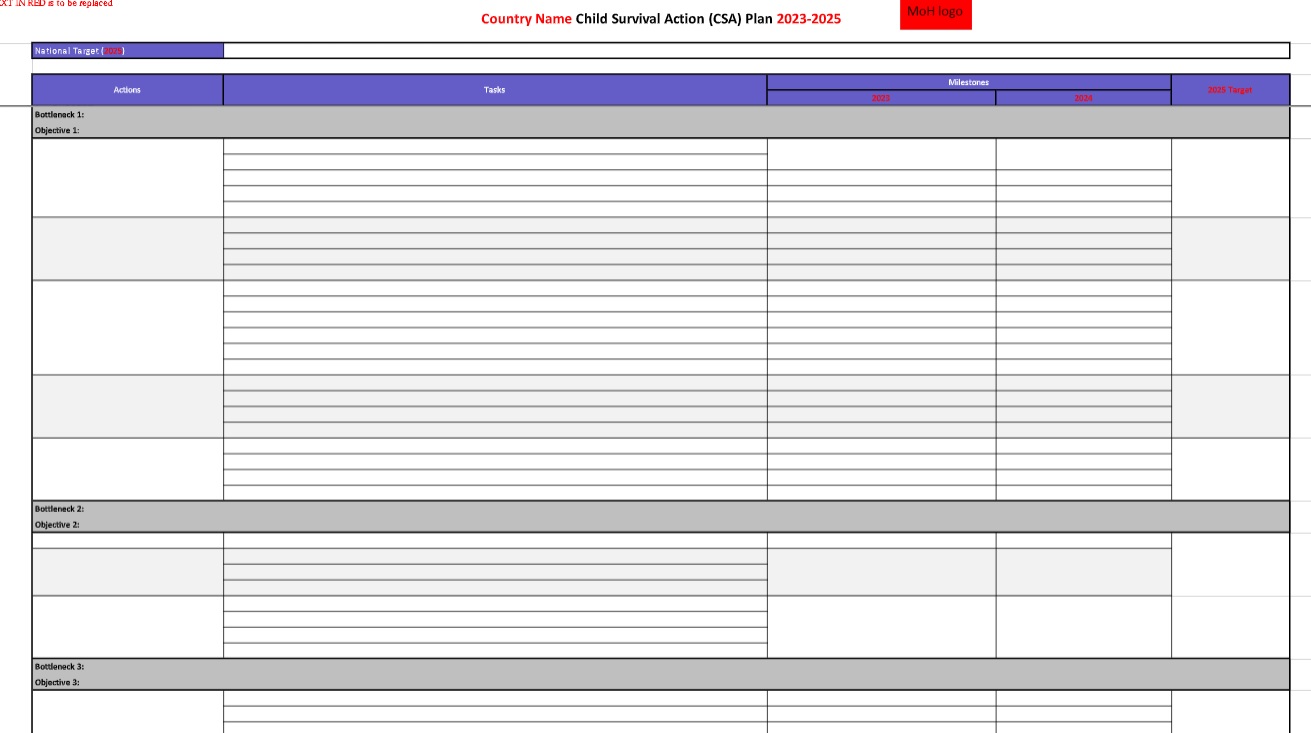
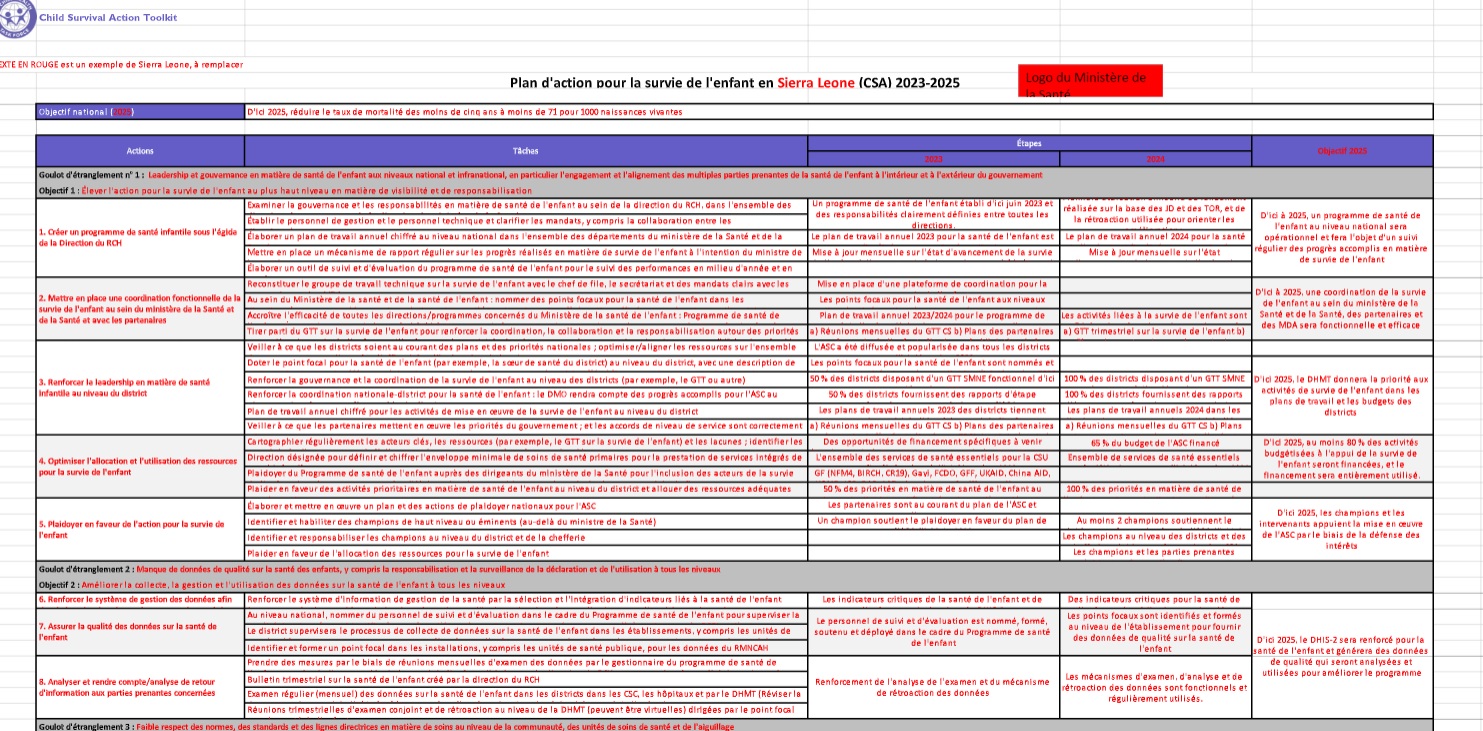
After priorities have been determined, they can be translated into priority action items within a medium-term plan. The process should include setting of objectives and key targets in line with identified priorities and the formulation of key actions (or activities) to achieve the objectives.
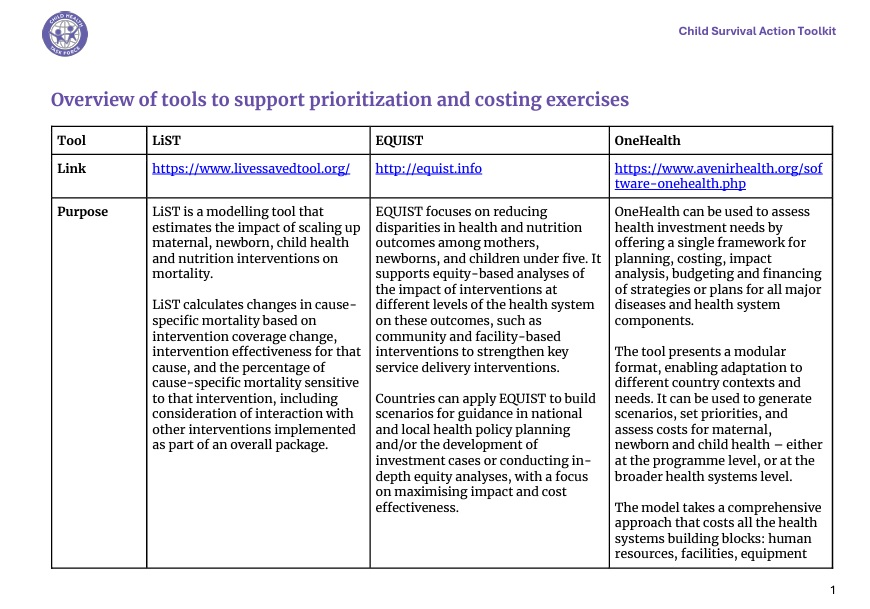
Costing is also an integral part of the planning process. Estimating the costs of a plan provides information on the financial resource needs for planned activities, allowing decision-makers to consider whether strategic activities are feasible and affordable. A mapping of relevant documents, including costing exercises from previous plans should be conducted to inform current cost projections. Projected costs can be compared to available financial resources to identify potential resource gaps. Costing is an iterative process, often requiring several rounds of discussion and calculation.
The tools and resources within this section can support countries with the process of setting priorities and strengthening and effectively costing plans for child survival.