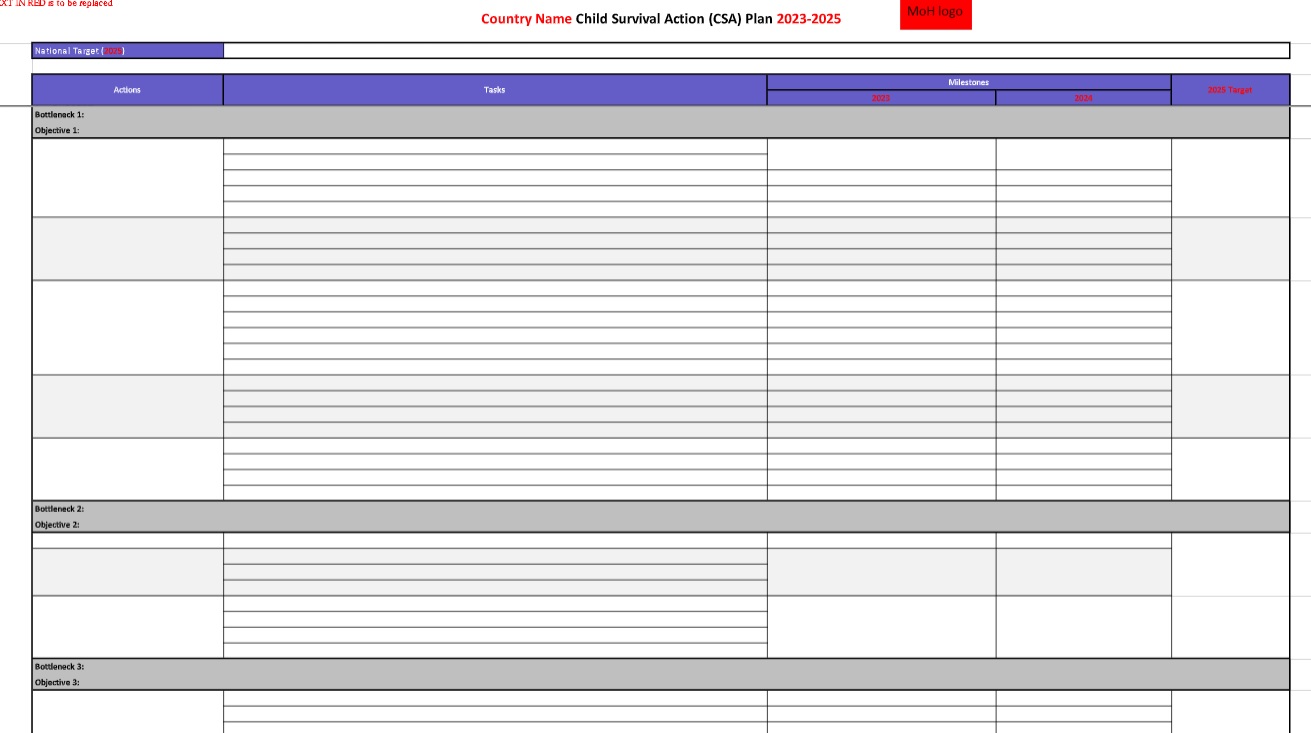
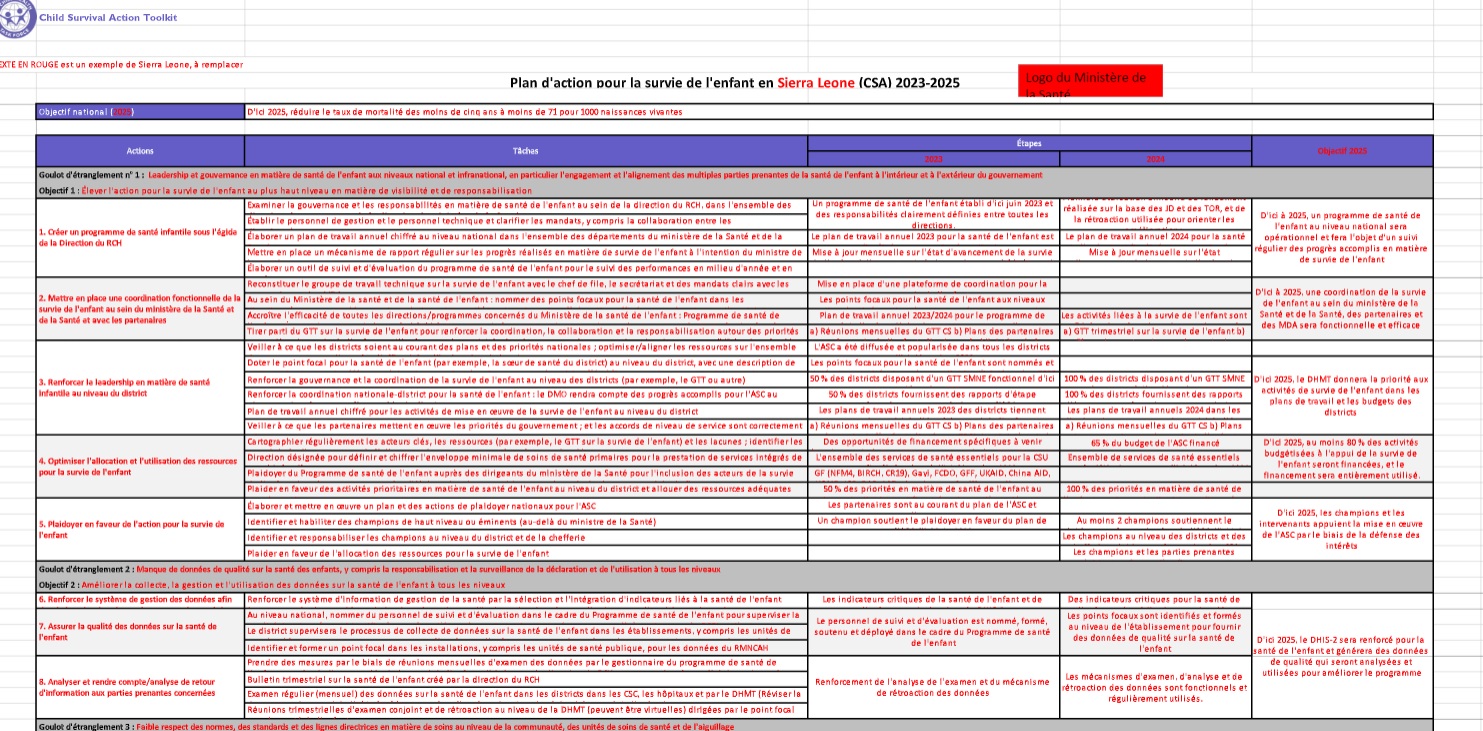
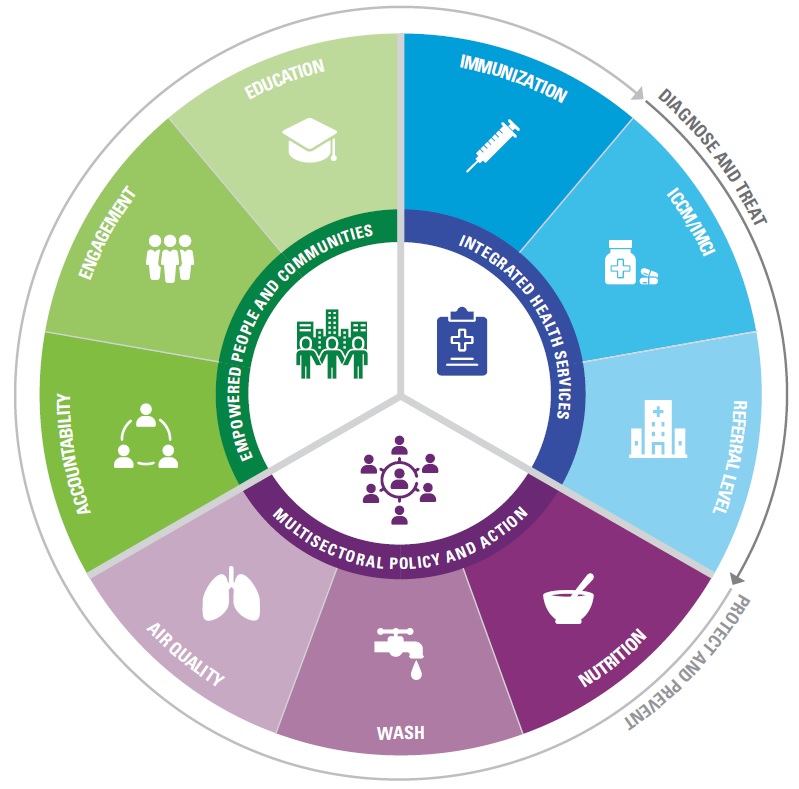
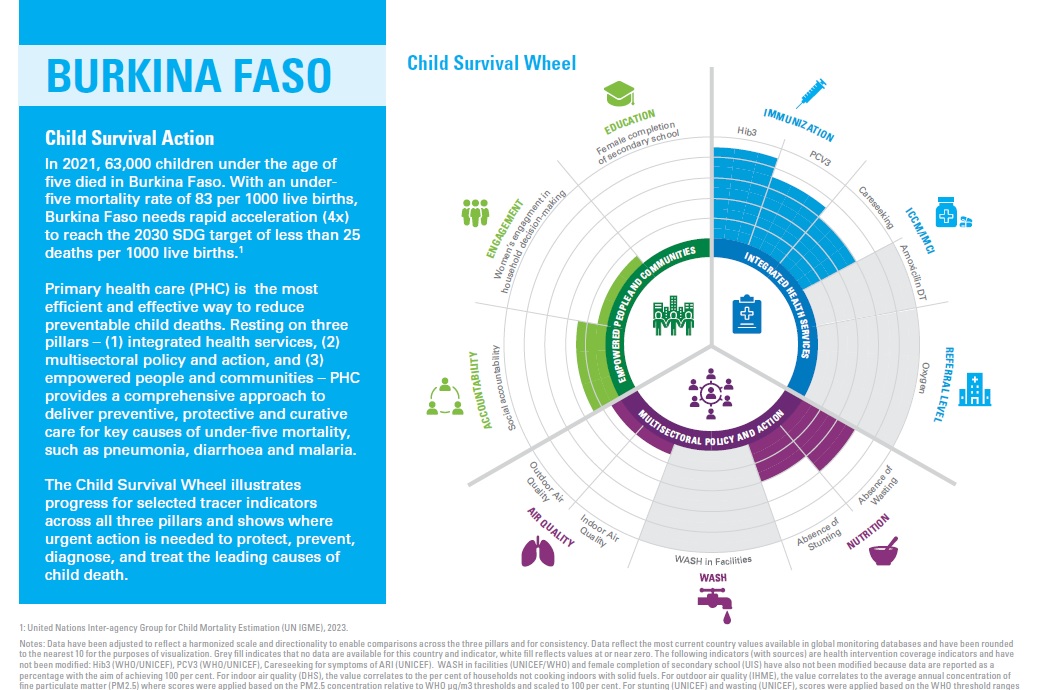
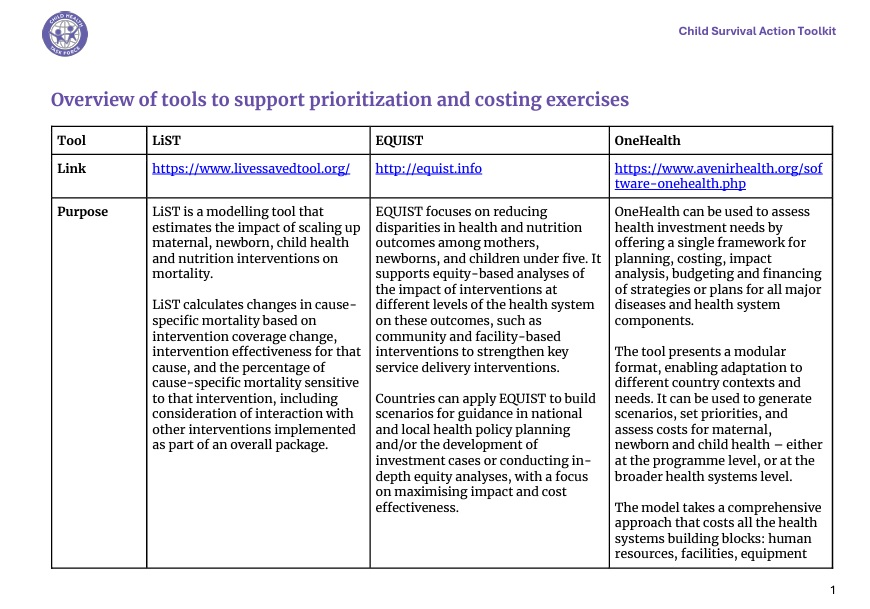
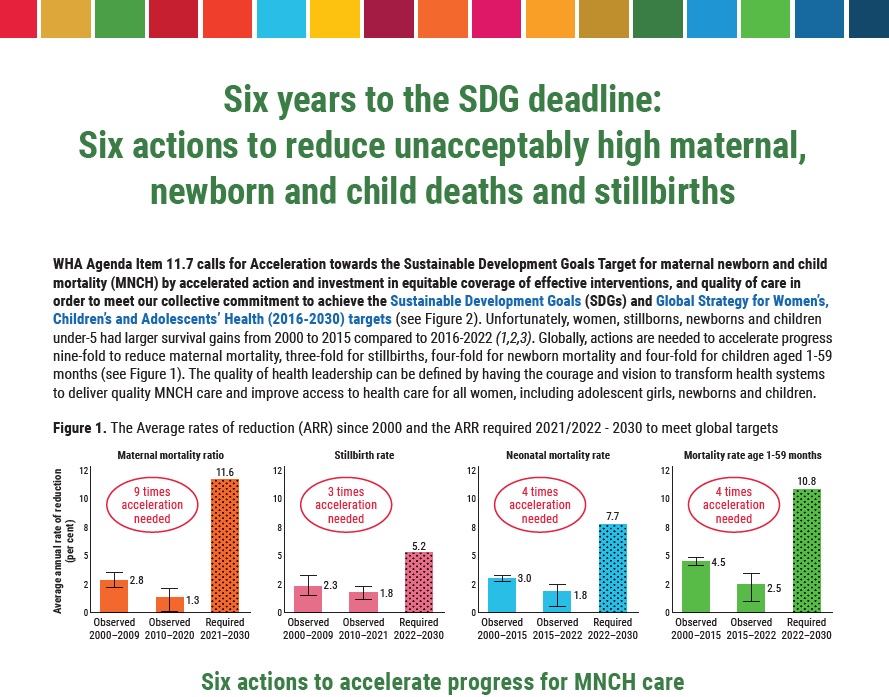
The Child Survival Action (CSA) Toolkit is designed to support countries with planning, sharpening, and implementing activities aimed at accelerating reductions in child mortality beyond the newborn period in their national contexts. It is intended to be a resource for all actors engaged in planning, costing, implementing, and monitoring child health activities, including, national and sub-national program managers, policy makers, academics, professional associations, non-governmental organizations, and international agencies.
Click on any of the five elements in the wheel to view those sections.
How to use this toolkit Background on CSA CSA Process Guide
Provide feedback on the Toolkit
Contact us for additional support at ChildSurvivalAction2030@gmail.com.
Search the CSA Toolkit
We found 61 resources for you to choose from.